Your How to work out initial velocity images are available in this site. How to work out initial velocity are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the How to work out initial velocity files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for how to work out initial velocity images information connected with to the how to work out initial velocity topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you hints for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
How To Work Out Initial Velocity. Then use the velocity formula to find the velocity. Final velocity 2 initial velocity 2 2 acceleration distance. Solve that and you will get the value. Next divide the distance by the time and write down that quotient as well.
 This Diagram Shows How To Calculate The X And Y Components Of The Initial Velocity Projectile Motion Velocity Initials From pinterest.com
This Diagram Shows How To Calculate The X And Y Components Of The Initial Velocity Projectile Motion Velocity Initials From pinterest.com
This initial rate of reaction can be expressed simply as a change in absorbance per unit of timeΔA410min. A v-u div t where. Formula for velocity as a function of initial velocity acceleration and time v u at u initial velocity v final velocity a acceleration t time Example. Finally subtract your first quotient from your second quotient to find the initial velocity. V is final velocity in ms. For example the square root of 286 equals 53 so the velocity is 53 ms.
The initial velocity of the train was 60 ms.
Since the initial velocity was zero the final velocity is equal to the change of speed. Formula for velocity as a function of initial velocity acceleration and time v u at u initial velocity v final velocity a acceleration t time Example. V is proportional to S B. For example the square root of 286 equals 53 so the velocity is 53 ms. Since the initial velocity was zero the final velocity is equal to the change of speed. U is initial velocity in ms.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Final velocity 2 initial velocity 2 2 acceleration distance. The initial velocity can be found using the formula. Velocity change 695 4 278 ms. Find time t given final velocity v initial velocity u and acceleration a A car approaching a school zone slows down from 27 ms to 9 ms with constant acceleration -2 ms 2. V i v f - at.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Typically velocity is calculated based on the work that has previously been done. V distance time 500m 180 seconds 277 msec. Then divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. Finally V doesnt increase anymore and velocity reaches its maximum V max i. Then you can find the time taken using v u a t.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
As S increases V increases less and less i. The sketch is shown at the right and the use of trigonometric functions to determine the. V is final velocity in ms. The ball moves up to a maximum point. Since acceleration and distance are given you can use v 2 2 a s.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Using a velocity calculator or an initial velocity calculator makes this task easier. U 0 ms 1 is the initial velocity a g ms 2 and s 370 m. Set initial velocity to zero youre not moving at the beginning of the race. The equation for acceleration can also be represented as. V i 300 ms - 040 ms 2600 s v i 300 ms - 240 ms v i 300 - 240 ms.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
As S increases V increases less and less i. The initial velocity of the train was 60 ms. You are trying to find the final velocity v. V is proportional to S B. How do I find the time when speed distance and acceleration are given.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
V is proportional to S B. Next divide the distance by the time and write down that quotient as well. Initial Velocity is the velocity at time interval t 0 and it is represented by u. Multiply the acceleration by time to obtain the velocity change. Final velocity v squared equals initial velocity u squared plus two times acceleration a times displacement s.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Finally V doesnt increase anymore and velocity reaches its maximum V max i. The equation for acceleration can also be represented as. 60 x 3 minutes 180 seconds. To find initial velocity start by multiplying the acceleration by the time. It is the velocity at which the motion starts.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
It is the velocity at which the motion starts. For example the square root of 286 equals 53 so the velocity is 53 ms. A Acceleration u Initial Velocity v Final Velocity t Time. Calculating the Acceleration when the Final Velocity the Initial Velocity and the Time is Given. Lets solve an example.
 Source: it.pinterest.com
Source: it.pinterest.com
To analyze the data you are collecting you will need to calculate initial velocity v0. The formula is s ut 05 at2 where s is the distance u is the initial velocity speed is the magnitude of velocity a is the acceleration and t is the time. When calculating the velocity of the object follow these steps. Since acceleration and distance are given you can use v 2 2 a s. Graeme Sequera teaches how to calculate initial velocity About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It is the velocity at which the motion starts. Then you can find the time taken using v u a t. The formula is s ut 05 at2 where s is the distance u is the initial velocity speed is the magnitude of velocity a is the acceleration and t is the time. The sketch is shown at the right and the use of trigonometric functions to determine the. It leaves the childs hand with a positive initial velocity v i.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Or you can use the calculator to check your answer. Finally subtract your first quotient from your second quotient to find the initial velocity. U 0 ms 1 is the initial velocity a g ms 2 and s 370 m. These are known as the horizontal and vertical components of the initial velocity. You are trying to find the final velocity v.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Lets solve an example. Initial Velocity is the velocity at time interval t 0 and it is represented by u. Finally subtract your first quotient from your second quotient to find the initial velocity. U is initial velocity in ms. Enzyme is working as fast.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
It leaves the childs hand with a positive initial velocity v i. A good average would require a review of at least three sprints. Velocity acceleration and distance This equation applies to objects in uniform acceleration. The formula is s ut 05 at2 where s is the distance u is the initial velocity speed is the magnitude of velocity a is the acceleration and t is the time. Solve that and you will get the value.
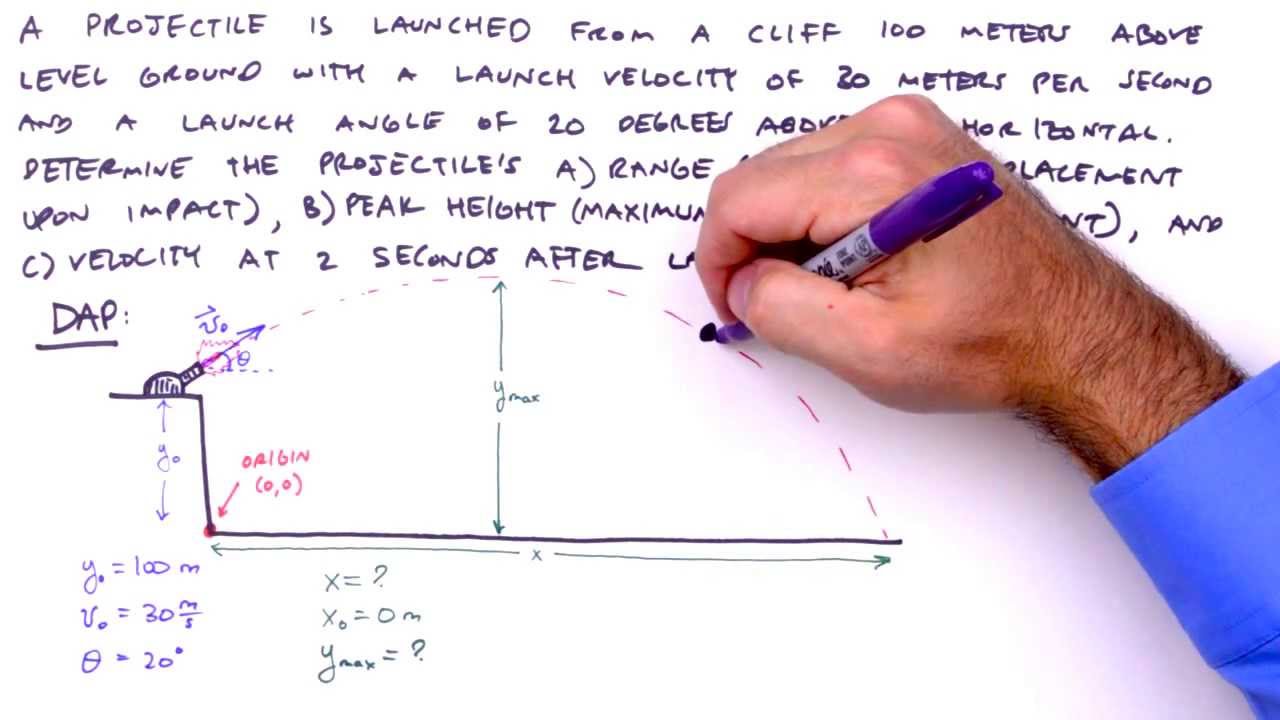 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Next divide the distance by the time and write down that quotient as well. This initial rate of reaction can be expressed simply as a change in absorbance per unit of timeΔA410min. The easiest is first to express velocity as the variation of absorbance per time unit typically velocity is expressed in min -1 as absorbance has no unit. A Acceleration u Initial Velocity v Final Velocity t Time. Then use the velocity formula to find the velocity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Then use the velocity formula to find the velocity. It is the velocity at which the motion starts. The easiest is first to express velocity as the variation of absorbance per time unit typically velocity is expressed in min -1 as absorbance has no unit. T is time in s. V distance time 500m 180 seconds 277 msec.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
As S is first increased the initial rate or velocity V 0 increases with increasing substrate concentration i. Find time t given final velocity v initial velocity u and acceleration a A car approaching a school zone slows down from 27 ms to 9 ms with constant acceleration -2 ms 2. It is the velocity at which the motion starts. Formula for velocity as a function of initial velocity acceleration and time v u at u initial velocity v final velocity a acceleration t time Example. Calculating the Acceleration when the Final Velocity the Initial Velocity and the Time is Given.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
First change the minutes into seconds. Velocity Equations for these calculations. The initial velocity can be found using the formula. Final velocity 2 initial velocity 2 2 acceleration distance. Final velocity v squared equals initial velocity u squared plus two times acceleration a times displacement s.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This initial rate of reaction can be expressed simply as a change in absorbance per unit of timeΔA410min. Formula for velocity as a function of initial velocity acceleration and time v u at u initial velocity v final velocity a acceleration t time Example. Then divide that number by 2 and write down the quotient you get. Solve that and you will get the value. V is proportional to S B.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how to work out initial velocity by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






