Your Explain how enzymes work images are available in this site. Explain how enzymes work are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Explain how enzymes work files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re searching for explain how enzymes work images information related to the explain how enzymes work topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our website always provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
Explain How Enzymes Work. Enzymes are essential for healthy digestion and a healthy body. Like all other catalysts enzymesare characterized by two fundamental properties. Enzymes work by lowering the Activation Energy of a reaction. This worksheet accompanies enzymesppt and digestive enzymesppt.
 What Is An Enzyme Cofactor From news-medical.net
What Is An Enzyme Cofactor From news-medical.net
Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. Explain how an enzyme works using the following terms Catalyst Enzyme Active Site Substrate and Product. The robot that was designed to move a car door cant put brakes on the car. Enzymes are like those giant robots.
They act as catalysts in order to help produce and speed up chemical reactions.
Once their job is done they move to the next piece and do the same thing again. Explain what eicosanoids are and how they are produced. What do enzymes do. Different enzymes are located in different areas of the body with each enzyme working on only. Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
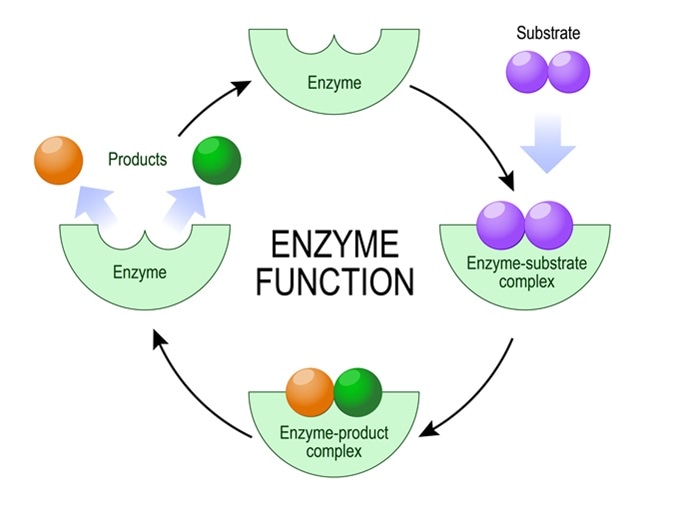
In general the working mechanism of an enzyme can be described as follows. They are little protein robots inside your cells. Each enzyme acts upon a specific target called substrate which is transformed into usable products through the action of the enzyme. In general the working mechanism of an enzyme can be described as follows. Enzymes are responsible for a lot of the work that is going on in cells.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
First week only 499. They are vital for life and serve a wide range of important functions in the body such as aiding in digestion and metabolism. What environmental factors affect enzyme activity. 62 How enzymes work continued Enzymes can work by. The robot that was designed to move a car door cant put brakes on the car.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Changing these alter the rate of reaction. The enzyme or the Catalyst works by combining with its substrate in the activation site and converts it to Products. Enzymes are like those giant robots. Holding the molecules the right way round so that the reactive groups are. The speed at which the chemical reaction occurs is determined by the action of the enzyme.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
They work with other chemicals in the body such as stomach acid and bile to help break down food into molecules for a wide range. What environmental factors affect enzyme activity. When the temperature is too high the enzymes are destroyed or denaturing What is denaturing and what causes it to occur. Enzymes are essential for healthy digestion and a healthy body. There are two categories of messengers namely hydrophilic and hydrophobic.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Enzymes work best within specific. The Activation Energy of a reaction is lowered by putting stress on the bonds within a molecule or by holding molecules close together. C The action of enzymes is often explained in terms of the lock and key model as shown in Fig. Second they increase reaction rates without altering the chemical equilibrium between reactants and products. Enzymes work by binding to reactant molecules and holding them in such a way that the chemical bond-breaking and bond-forming processes take place more readily.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
First they increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. Summary Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. 62 How enzymes work continued Enzymes can work by. Like all other catalysts enzymesare characterized by two fundamental properties. They grab one or two pieces do something to them and then release them.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. Explain what eicosanoids are and how they are produced. _Image modified from Potential kinetic free and activation energy. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Enzymes are like those giant robots. Explain how an enzyme works using the following terms Catalyst Enzyme Active Site Substrate and Product. They act as catalysts in order to help produce and speed up chemical reactions. A catalyst is a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction by reducing the amount of energy needed to start that reaction. However if the optimum temperature is surpassed the.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
When a molecule enters the active site a chemical reaction takes place. Like all other catalysts enzymesare characterized by two fundamental properties. Enzymes are the biological substance proteins that act as CATALYSTS and help complex reactions occur everywhere in life. Enzymes work by lowering the Activation Energy of a reaction. Solution for The glucose biosensor is an enzyme biosensor and explains how it work.
 Source: news-medical.net
Source: news-medical.net
First they increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. Second they increase reaction rates without altering the chemical equilibrium between reactants and products. They grab one or two pieces do something to them and then release them. In other words the enzyme reacts with the substrate forming an enzyme-substrate complex.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This worksheet accompanies enzymesppt and digestive enzymesppt. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. Temperature is increased the activity will increase. They are vital for life and serve a wide range of important functions in the body such as aiding in digestion and metabolism.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Start your trial now. Once the reaction is complete the enzyme remains the same. Explain what eicosanoids are and how they are produced. Enzymes are responsible for a lot of the work that is going on in cells. However if the optimum temperature is surpassed the.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
This increases the likelihood of a reaction and so lowers the energy required to begin it. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. The activities of enzymes depend on the temperature ionic conditions and the pH of the surroundings. Enzymes work by lowering the Activation Energy of a reaction. Enzymes work by creating a location for molecules to bind together or break apart called the active site.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
First week only 499. They work with other chemicals in the body such as stomach acid and bile to help break down food into molecules for a wide range. C The action of enzymes is often explained in terms of the lock and key model as shown in Fig. Once their job is done they move to the next piece and do the same thing again. 32 Use the information in Fig.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
32 to explain how enzymes work to break down nutrient materials such as starch. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. Once the reaction is complete the enzyme remains the same. Second they increase reaction rates without altering the chemical equilibrium between reactants and products. Explain what eicosanoids are and how they are produced.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are. This is called lowering the activation energy. Include the term activation energy and compare the two curves explaining which is with the enzyme. What environmental factors affect enzyme activity. This worksheet accompanies enzymesppt and digestive enzymesppt.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Summary Enzymes work by lowering the activation energy needed to start biochemical reactions. Enzymes are Specific Enzymes are very specific. First week only 499. Some enzymes help break large molecules into smaller pieces that are. This is called lowering the activation energy.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
C The action of enzymes is often explained in terms of the lock and key model as shown in Fig. This is called lowering the activation energy. First they increase the rate of chemical reactions without themselves being consumed or permanently altered by the reaction. The speed at which the chemical reaction occurs is determined by the action of the enzyme. Enzymes work by creating a location for molecules to bind together or break apart called the active site.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title explain how enzymes work by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






