Your Arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work images are ready. Arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work pictures information connected with to the arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work topic, you have visit the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video content and graphics that match your interests.
Arterial Baroreceptor Afferent Fibres Work. We have conducted both reductive studies of mechanoelectrical transduction in cultured baroreceptor neurons and integrative studies with in vivo recordings of the activity of baroreceptor afferent fibers and efferent sympathetic nerves. The arterial baroreceptor reflex utilizes all these mechanisms in a coordinated manner to main- tain arterial pressure at a steady level. What are the steps of baroreceptor reflex. The baroreceptor reflex works through the autonomic nervous system ANS.
 Schematic Diagram Of Aortic And Carotid Baroreceptor Terminals And Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Schematic Diagram Of Aortic And Carotid Baroreceptor Terminals And Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
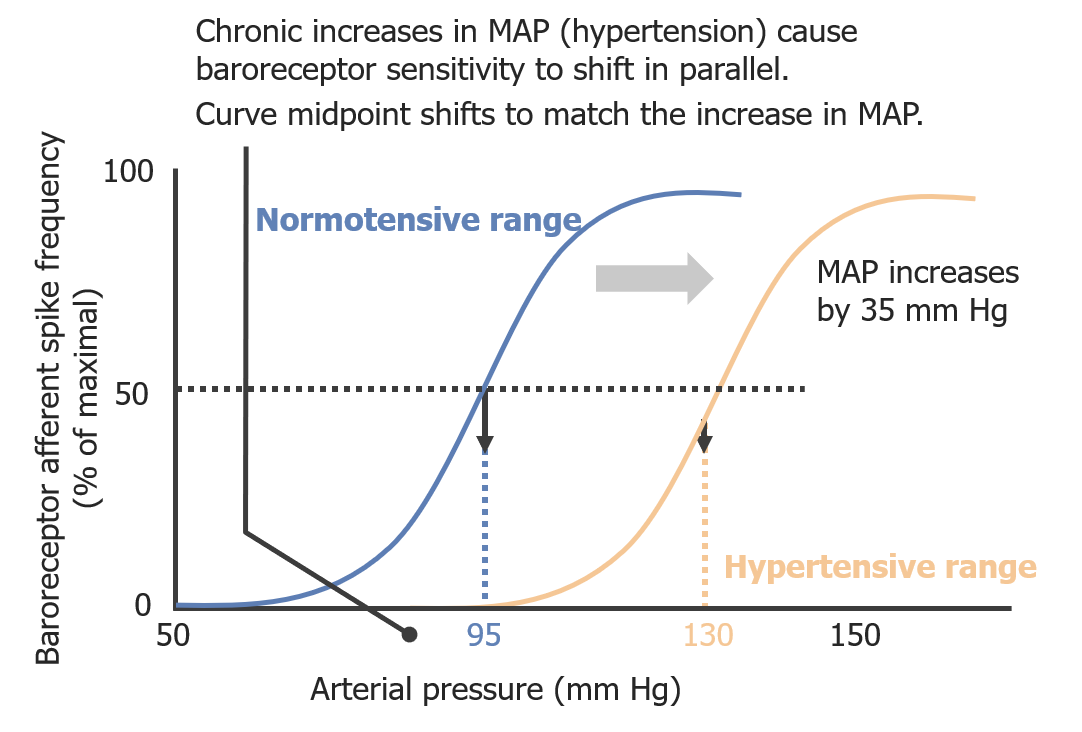
We have examined whether the relationship between mean baroreceptor discharge and mean arterial pressure is altered when heart rate changes. Stress and strain in the wall of the artery are determined by the arterial pressure and it is. Please note the baroreceptor activity increases as arterial blood pressure increases following the injection of the vasopressor A. The carotid sinus receptors respond to pressures ranging from 60-180 mmHg Figure 2. The afferent fibers from aortic baroreceptors pass centrally via the vagus nerves. The arterial baroreceptors and their afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the reflex that regulates systemic arterial pressure.
Alternatively substance P may have been released directly from skeletal muscle afferent fibres and arterial baroreceptors that projected to the cNTS.
Meanwhile there are extra-carotid arterial baroreceptors found in the aortic arch and stretch. This decreased blood pressure leads to fewer signals to be sent to stretch fibers in the aortic arch via the vagus nerve and carotid sinus via the glossopharyngeal nerve. The baroreceptors can identify the changes in both the average blood pressure or the rate of change in pressure with each arterial pulse. The baroreceptor reflex works through the autonomic nervous system ANS. We have examined whether the relationship between mean baroreceptor discharge and mean arterial pressure is altered when heart rate changes. Thus there are decreased inputs sent.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
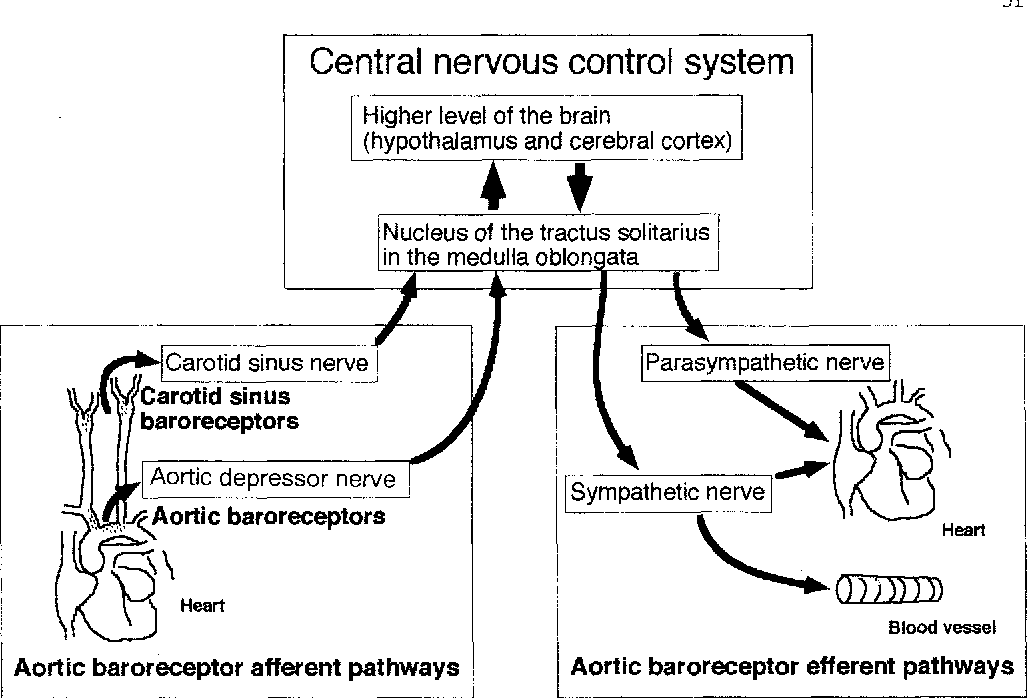
There are two primary sites that contain clusters of arterial baroreceptors. Afferent vagal and glssopharyngeal nerve fibres and efferent vagal and sympathetic fibres complete the reflex arc. Glutamate regulates its own release by activating presynaptic metabotropic glutamate autoreceptors mGluRs on the baroreceptor central terminals to suppress its further release in frequency-dependent manner. 1-7 It has four main components. Afferent fibers from these carotid sinus baroreceptors join their respective glossopharyngeal nerve and project to the nucleus tractus solitarii in the dorsal medulla which is under cortical command.
 Source: semanticscholar.org
Source: semanticscholar.org
Meanwhile there are extra-carotid arterial baroreceptors found in the aortic arch and stretch. As is typical with any reflex the arterial baroreflex is composed of neural sensors afferent path- ways central integrating. Baroreceptor activity returns to baseline level upon attaining homeostatic arterial pressure. Baroreceptors are strecth-sensitive mechanoreceptors sited at the aortic arch and carotid sinus which are used to regulate arterial blood pressure by a negative feedback loop. Baroreceptors are mechanosensitive afferent nerve endings that are interspersed in the arterial elastic layers.
 Source: mdpi.com
Source: mdpi.com
Afferent nerve fibers nerves that carry pressure signals from the baroreceptor to the brain. They are as follows. We have examined whether the relationship between mean baroreceptor discharge and mean arterial pressure is altered when heart rate changes. The nucleus of the solitary tract appears to be the main processor. Of these two sites for arterial baroreceptors the carotid sinus is quantitatively the most important for regulating arterial pressure.
 Source: prohealthinsight.com
Source: prohealthinsight.com
The arterial baroreceptors and their afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the reflex that regulates systemic arterial pressure. The baroreceptors can identify the changes in both the average blood pressure or the rate of change in pressure with each arterial pulse. Glutamate regulates its own release by activating presynaptic metabotropic glutamate autoreceptors mGluRs on the baroreceptor central terminals to suppress its further release in frequency-dependent manner. Afferent fibers from these carotid sinus baroreceptors join their respective glossopharyngeal nerve and project to the nucleus tractus solitarii in the dorsal medulla which is under cortical command. Action potentials triggered in the baroreceptor ending are then directly conducted to the brainstem where central.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The carotid sinus receptors respond to pressures ranging from 60-180 mmHg Figure 2. This decreased blood pressure leads to fewer signals to be sent to stretch fibers in the aortic arch via the vagus nerve and carotid sinus via the glossopharyngeal nerve. There are two primary sites that contain clusters of arterial baroreceptors. Maximal carotid sinus sensitivity occurs. The primary baroreceptor afferent fibres make their first excitatory synaptic contact at second-order NTS neurones with glutamate as the major neurotransmitter.
 Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Afferent fibers from these carotid sinus baroreceptors join their respective glossopharyngeal nerve and project to the nucleus tractus solitarii in the dorsal medulla which is under cortical command. Baroreceptors are strecth-sensitive mechanoreceptors sited at the aortic arch and carotid sinus which are used to regulate arterial blood pressure by a negative feedback loop. Arterial baroreceptors are stretch receptors that are stimulated by distortion of the arterial wall when pressure changes. Increased AP induces expansion or contraction in the baroreceptors and facilitates the arterial baroreceptors afferent discharge to transmit signals. The internal carotid artery at the carotid sinus carotid sinus baroreceptors and.
 Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Source: nyaspubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com
Maximal carotid sinus sensitivity occurs. What are the steps of baroreceptor reflex. Arterial baroreceptors are stretch receptors that are stimulated by distortion of the arterial wall when pressure changes. The arterial baroreflex normally regulates the blood pressure and heart rate through sensing changes of arterial vascular tension by the arterial baroreceptors in the aortic arch and carotid sinus. The primary baroreceptor afferent fibres make their first excitatory synaptic contact at second-order NTS neurones with glutamate as the major neurotransmitter.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The nucleus of the solitary tract appears to be the main processor. The carotid sinus receptors respond to pressures ranging from 60-180 mmHg Figure 2. Alternatively substance P may have been released directly from skeletal muscle afferent fibres and arterial baroreceptors that projected to the cNTS. Therefore it is more likely that. While the baroreceptor reflex is often used in specific reference to the reflexive change in ABP and heart rate brought about by changing autonomic outflow to the heart and vasculature there are a large number of physiological.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
As is typical with any reflex the arterial baroreflex is composed of neural sensors afferent path- ways central integrating. What are the steps of baroreceptor reflex. Thus there are decreased inputs sent. When the baroreflex afferents are abnormally activated such as by paragangliomas in the neck presumably by direct. Afferent fiber types of BRNs isolated from the NG of adult female rats were identified by using electrophysiological pharmacological validation and Dil labeling.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
The baroreceptor reflex works through the autonomic nervous system ANS. The baroreceptors can identify the changes in both the average blood pressure or the rate of change in pressure with each arterial pulse. Of these two sites for arterial baroreceptors the carotid sinus is quantitatively the most important for regulating arterial pressure. Afferent nerve fibers nerves that carry pressure signals from the baroreceptor to the brain. What are the steps of baroreceptor reflex.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
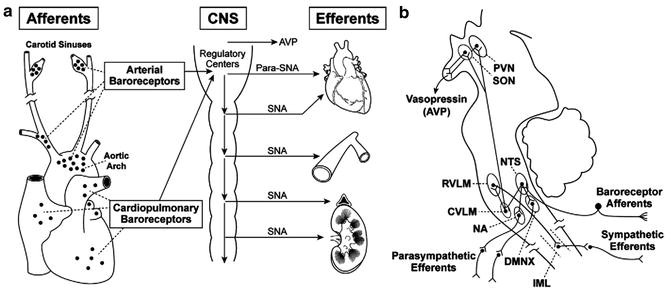
Impulses originating in the aortic arch travel along afferent fibers of the vagus nerve to synapse at the NTS. Increased AP induces expansion or contraction in the baroreceptors and facilitates the arterial baroreceptors afferent discharge to transmit signals. Afferent fiber types of BRNs isolated from the NG of adult female rats were identified by using electrophysiological pharmacological validation and Dil labeling. When the afferent fibers of the baroreflex are injured by surgery or radiotherapy or fail to develop as in familial dysautonomia their sensory information is no longer present to regulate arterial blood pressure resulting in afferent baroreflex failure. Results suggest that the primary mechanism of mechanical activation of baroreceptor neurons involves opening of stretch.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The term arterial baroreceptor reflex is used to refer to a variety of physiological responses elicited by changes in baroreceptor afferent activity. In turn they project to efferent cardiovascular neurons in the medulla and spinal cord. Results suggest that the primary mechanism of mechanical activation of baroreceptor neurons involves opening of stretch. When the afferent fibers of the baroreflex are injured by surgery or radiotherapy or fail to develop as in familial dysautonomia their sensory information is no longer present to regulate arterial blood pressure resulting in afferent baroreflex failure. Baroreceptors are mechanosensitive afferent nerve endings that are interspersed in the arterial elastic layers.
 Source: lecturio.com
Source: lecturio.com
The arterial baroreceptors and their afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the reflex that regulates systemic arterial pressure. Baroreceptors detect mechanical deformation of the vessel wall ie vascular wall stretch due to changes in intraluminal pressure. Thus there are decreased inputs sent. Action potentials triggered in the baroreceptor ending are then directly conducted to the brainstem where central. Of these two sites for arterial baroreceptors the carotid sinus is quantitatively the most important for regulating arterial pressure.
 Source: link.springer.com
Source: link.springer.com
They are as follows. Hemorrhage on the other hand causes a decrease in blood pressure. Baroreceptor afferents from the carotid sinus travel in the carotid sinus nerve Herings nerve before joining the glossopharyngeal nerve. The arterial baroreflex mechanism is explored in this chapter. As is typical with any reflex the arterial baroreflex is composed of neural sensors afferent path- ways central integrating.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Terms in this set 5 Increase of heart rate force of ventricular contraction. In turn they project to efferent cardiovascular neurons in the medulla and spinal cord. We have conducted both reductive studies of mechanoelectrical transduction in cultured baroreceptor neurons and integrative studies with in vivo recordings of the activity of baroreceptor afferent fibers and efferent sympathetic nerves. Afferent fibers from these carotid sinus baroreceptors join their respective glossopharyngeal nerve and project to the nucleus tractus solitarii in the dorsal medulla which is under cortical command. The arterial baroreceptors and their associated afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the first order baroreflex control of arterial pressure.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The arterial baroreceptors and their afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the reflex that regulates systemic arterial pressure. The baroreceptor reflex works through the autonomic nervous system ANS. Of these two sites for arterial baroreceptors the carotid sinus is quantitatively the most important for regulating arterial pressure. Baroreceptors are strecth-sensitive mechanoreceptors sited at the aortic arch and carotid sinus which are used to regulate arterial blood pressure by a negative feedback loop. What are the steps of baroreceptor reflex.
 Source: n.neurology.org
Source: n.neurology.org
The arterial baroreceptors and their afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the reflex that regulates systemic arterial pressure. As is typical with any reflex the arterial baroreflex is composed of neural sensors afferent path- ways central integrating. Thus stimu- lation of arterial baroreceptors or their afferent fibers is a reliable means of producing well-controlled per- turbations on these efferent mechanisms easily and repeatedly. Arterial Baroreceptors Impulses sent via the carotid sinus transmit along the carotid sinus nerve to the glossopharyngeal nerve which synapses with the NTS in the medulla. The arterial baroreceptors and their associated afferent fibres provide the sensory arm of the first order baroreflex control of arterial pressure.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The arterial baroreflex normally regulates the blood pressure and heart rate through sensing changes of arterial vascular tension by the arterial baroreceptors in the aortic arch and carotid sinus. Terms in this set 5 Increase of heart rate force of ventricular contraction. Arterial baroreceptors are stretch receptors that are stimulated by distortion of the arterial wall when pressure changes. Afferent fibers from these carotid sinus baroreceptors join their respective glossopharyngeal nerve and project to the nucleus tractus solitarii in the dorsal medulla which is under cortical command. Results suggest that the primary mechanism of mechanical activation of baroreceptor neurons involves opening of stretch.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title arterial baroreceptor afferent fibres work by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






